
The VOOL ETF tracks the VIX Futures via a methodology called Enhanced Roll.

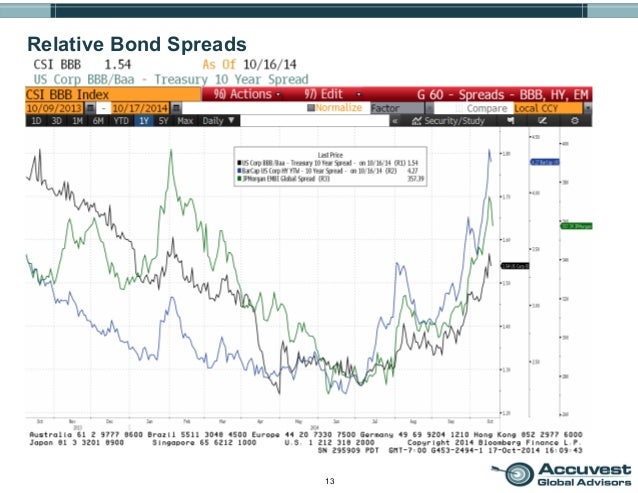
The highest intraday value that the VIX ever reached was 89.53 during the financial crisis in 2008. To put this number in perspective, the highest VIX close was 82.69 on the 16th of March 2020. Hence, a VIX around 15 indicates a relatively low volatility environment. From a monthly perspective, this indicates that the S&P 500 index could increase or decrease by 1.25%(=15%/12) in the next 30-day period. Before the COVID-crisis in March the VIX was around 15, which indicates the expected annualized change in the S&P 500 index. The VIX is often referred to as the Fear Index, as a higher value indicates higher levels of risk, fear or stress in the market. The VIX-index measures the implied volatility for options with the S&P 500 index as underlying. Find more information in the appendix below or in the product specification. Hence, make sure you understand the VOOL ETF before investing in it. However bear in mind that, even with this volatility allocation, there is still a risk of losing money. If you are afraid of upcoming events and want to protect against drawdown, consider a long VOOL position in that period. Hence, investors could consider a small long position in volatility as a hedge in turmoiled markets. The Sharpe Ratio is calculated without using the risk-free rate.Ĭomparing the portfolio without and with the volatility instrument shows that a long position in volatility protects you from larger drawdowns, on the cost of a drag on the portfolio performance in calmer markets. The return and standard deviation are annualized.

Comparison of portfolio without and with position in volatility. This is a metric that compares the realized return relative to the volatility (standard deviation) of the portfolio. Moreover, the Sharpe Ratios is also higher for the portfolio with long VOOL. The table below shows that the portfolio with a long position in the VOOL has less extreme drawdowns than the 60/40 portfolio. If volatility increases, mostly when markets go down, you’ll enjoy a negative correlation from the VOOL ETF. The premium paid for exposure to volatility can be seen as an insurance premium in case volatility changes. In 2020, markets have been volatile due to the COVID crisis and the US Election. In 2018, stock markets performed poorly due to uncertainty around Brexit and the trade war between the US and China. In 2015, we saw a global stock selloff due to a slowdown in the Chinese economy, the Greek debt default crisis and rising yields in the US (FED turned Hawkish). Comparison returns of portfolio without and with position in volatility In the last 8 years, portfolio 1 realized higher annualized returns than portfolio 2 except for 2015 (roughly the same return), 20. Historical performance portfolio with VOOL All instruments used in these portfolios are tradable for retail-clients. There is no strong reason to allocate precisely 4% of the portfolio to volatility, investors can use other fractions instead. Portfolio 2, has the same 60% equity allocation but reduced its bond holding by 4% and allocated this fraction into a long VOOL position.
Portfolio 1 has an allocation of 60% to equities and 40% to government bonds by going long the MSCI World Index (EUR Hedged) and European 7-10 year Government Bonds respectively.
In the next paragraph, we describe two portfolios. Therefore investors should consider reducing their fixed income position and invest this reduced fraction in a long volatility position. However, in certain scenarios with high market uncertainty, both of these positions may have negative returns, so one way to hedge is to include a small exposure to the VIX index. Historically the 40% in fixed income acted as a stabilizer as governmental bonds tend to have relatively lower volatility and rise in times of market stress, and they tend to increase in value when equities have negative returns. Portfolio with long position in VolatilityĪ traditional investment strategy is to use the 60/40 portfolio, where 60% of your portfolio is invested in equities and 40% in government bonds.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
